01.04.2025
Data-driven efficiency, productivity and competitiveness
Sensoridatan hyödyntäminen navigoinnissa
Project has investigated the feasibility of an inertial navigation system (INS) for small IoT devices. INS in general is a system that uses accelerometers and gyroscopes to determine the position, velocity and direction of an object without external references, such as GPS signals.
INS systems have generally recognized limitations:
- Accumulated Errors: INS relies on continuous measurements from accelerometers and gyroscopes. Over time, small errors in these measurements accumulate, leading to drift in position and orientation estimates
- Initial Calibration: Accurate initial calibration is crucial. Any errors during calibration can significantly affect the system's accuracy
- Sensitivity to External Forces: INS can be affected by external forces such as vibrations and shocks, which can introduce errors
- Cost and Complexity: High-precision INS systems can be expensive and complex to integrate and maintain
- Limited Long-Term Accuracy: Without external updates (e.g., GPS), INS accuracy degrades over time, making it less reliable for long-term navigation
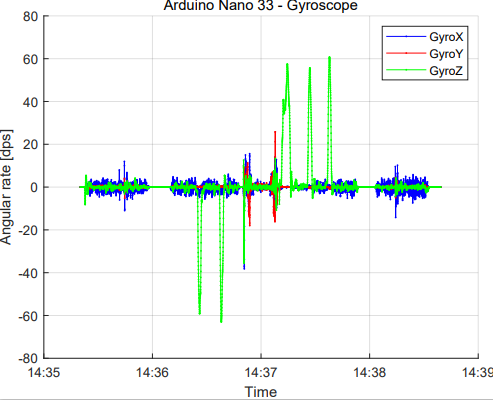
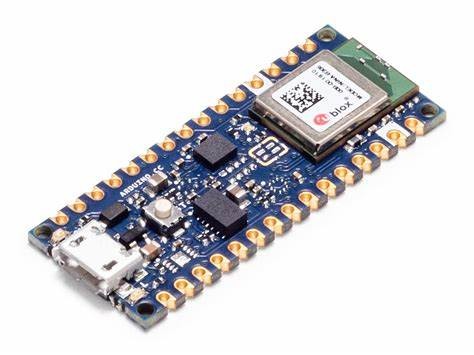
The Arduino Nano BLE sense Rev 2. device has been used as a test sensor board in the case. It contains several sensors needed for inertial navigation, such as an accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer. It also has Bluetooth for wireless connection. The inertial sensors on the board produce data at several hundred measurements per second.
The challenge is processing the data to convert it, for example, into direction and positioning. After processing the data, the information can be collected in a gateway device, for example, to visualize it.
News related cases
IoT sensor devices in data-driven process optimization